የኢትዮጵያ ምግብ
AN INTRODUCTION TO ETHIOPIAN'S TRADITIONAL CUSINE
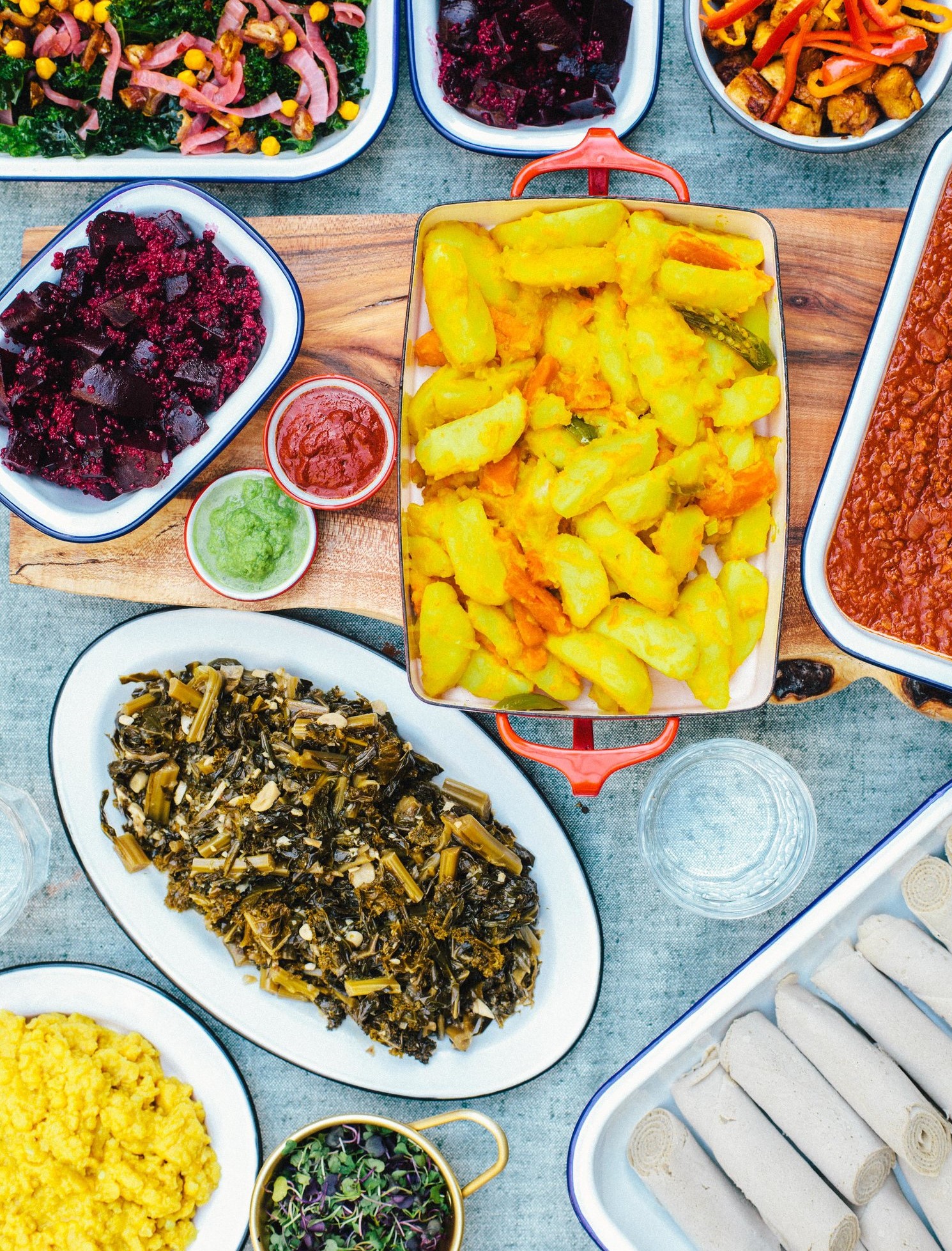
Ethiopian cusine consists of vegetable and meat side dishes and entrees,often prepared as a wot (thick stew).One or more servings of stew are placed upon a piece of INJERA , a large sourdough flatbread teff flour.One does not eat utensils,but instead uses the INJERA(always with the right hand)to scoop the food in to the bread.
Injera is a sourdough-risen and spongy flatbread that is a staple in Ethiopia. It relies on flour made from teff, which is part of the lovegrass family, and produces seeds as tiny as poppy seeds. It is nutrient-dense and gluten-free. Injera is served with stews, both meat-based and vegetarian; a torn-off piece of the flatbread is used to pick up the accompaniments
Ethiopian food is one of the most exciting cuisines in the world. Not only is the food extremely unique and extraordinarily flavorful, but the food culture that makes up Ethiopia is also something I found truly fascinating. To begin with, Ethiopian food is eaten with friends and family.Even the way Ethiopian food is served, on a communal platter, is designed for sharing food with each other. Food is not meant to be eaten alone in the culture of Ethiopia.